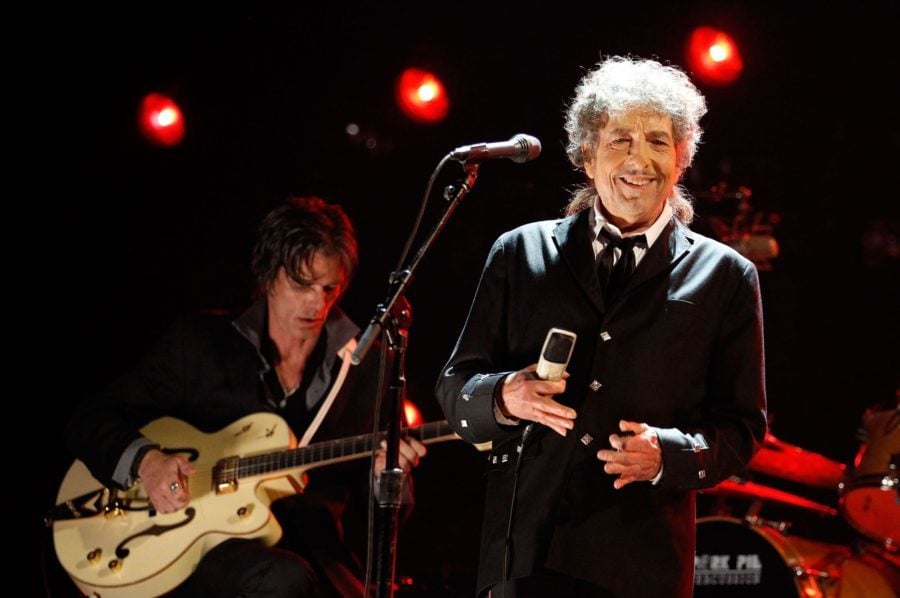
It ain’t no lie.
Bob Dylan has sold his immense collection of songs. The financial details were not disclosed, but most commentators estimate the deal is worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
While one song Dylan did not write was “Taxman” (that was George Harrison), he may have been thinking about that when deciding to go through with this sale. (While “Johnny’s in the basement mixing up the medicine,” Dylan was “on the pavement thinking about the government.”)
In fact, Dylan may have had his eye specifically on year-end tax planning as an added incentive here since he was able to lock-in today’s low tax rates. Even on this kind of gigantic capital gain, the top federal tax bill will only be 23.8% (the 20% long-term capital gain rate plus the 3.8% tax on net investment income = 23.8%), plus any applicable state income taxes.
Who knows what future tax rates might climb to on this kind of wealth? This is why so many people are considering year-end Roth conversions. At a minimum, today’s low tax rates can be locked-in without having to worry about the uncertainty of what future higher rates may do to people’s retirement savings. This is especially important for wealthier people who are most likely to be hit with tax increases.
Dylan did something else interesting here. He not only will pay a relatively low capital gain rate for 2020, but that is a one-time tax hit. He has effectively exchanged future ordinary income tax rates for today’s low capital gain rate. That is always a good tax plan.
Now that he has sold, he will no longer receive whatever annual income his song catalog generates in the future, since “when you ain’t got nothin’, you got nothin’ to lose.” That would have been taxed at 37% at today’s tax rates and maybe much higher if future tax rates increase on top earners like Dylan. That is very likely.
Dylan’s sale takes the entire value of his song collection out of his estate. Yes, it is replaced with gobs of cash, but that is much easier to value.
There will be no extended legal and tax battles with the IRS over the estate tax value of the song collection at death. This means less problems for heirs and possibly a lower estate tax bill than even the cash left in the estate might generate. Plus, the cash can more easily be distributed to his family. He will still have a large estate, but more manageable and easier to plan for.
The cash can be available for a wider variety of estate planning strategies, whether it be charitable planning or other wealth transfer vehicles. It’s just easier to work with cash than intangible property of uncertain value. Estate taxes can be better planned for.
While the celebrity and dollar amount here make interesting reading, advisors with wealthy clients might want to do similar types of last-minute year-end planning to reduce potentially higher future income and estate taxes.
After all, “you don’t need a weatherman to know which way the wind blows.”
For more information on Ed Slott, Ed Slott’s 2-Day IRA Workshop and , please visit www.IRAhelp.com

Relationships are key to our business but advisors are often slow to engage in specific activities designed to foster them.

Whichever path you go down, act now while you're still in control.

Pro-bitcoin professionals, however, say the cryptocurrency has ushered in change.

“LPL has evolved significantly over the last decade and still wants to scale up,” says one industry executive.

Survey findings from the Nationwide Retirement Institute offers pearls of planning wisdom from 60- to 65-year-olds, as well as insights into concerns.
Streamline your outreach with Aidentified's AI-driven solutions
This season’s market volatility: Positioning for rate relief, income growth and the AI rebound